
• Aspartate aminotransferases (AST) and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) are sometimes used as markers for tissue damage, though nonspecific (both enzymes are found diffusely throughout the body in various tissue types).
AST: transfers amino groups from aspartate to α-ketoglutarate (part of citric acid cycle), found in cytosol and mitochondria
LDH: converts pyruvate to lactate, found in cytosol
Clinically, AST is often used in the diagnosis of liver diseases as part of the liver function tests (LFTs) and LDH is used to diagnose hemolytic anemias and hematologic malignancies
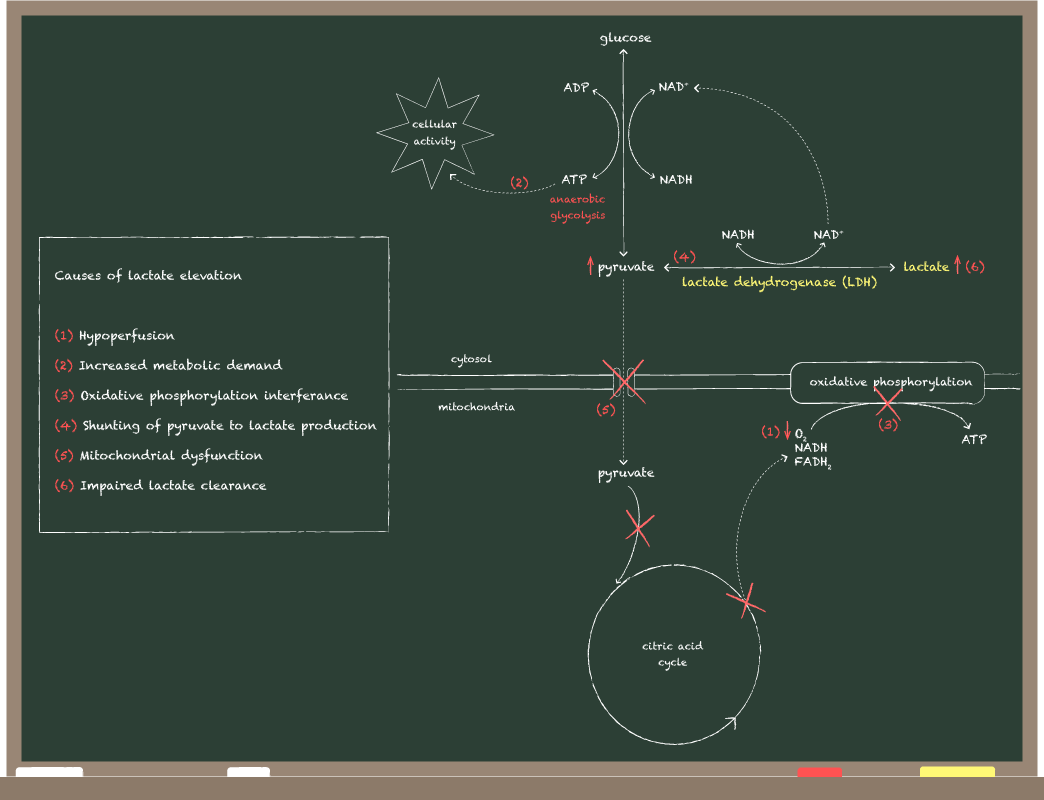
• On the other hand, lactate, which is converted from pyruvate by LDH during anaerobic glycolysis, is often used as a marker for tissue hypoperfusion/ ischemia.
However, lactate is also elevated in impaired cellular metabolism in the absence of tissue hypoperfusion/ ischemia.
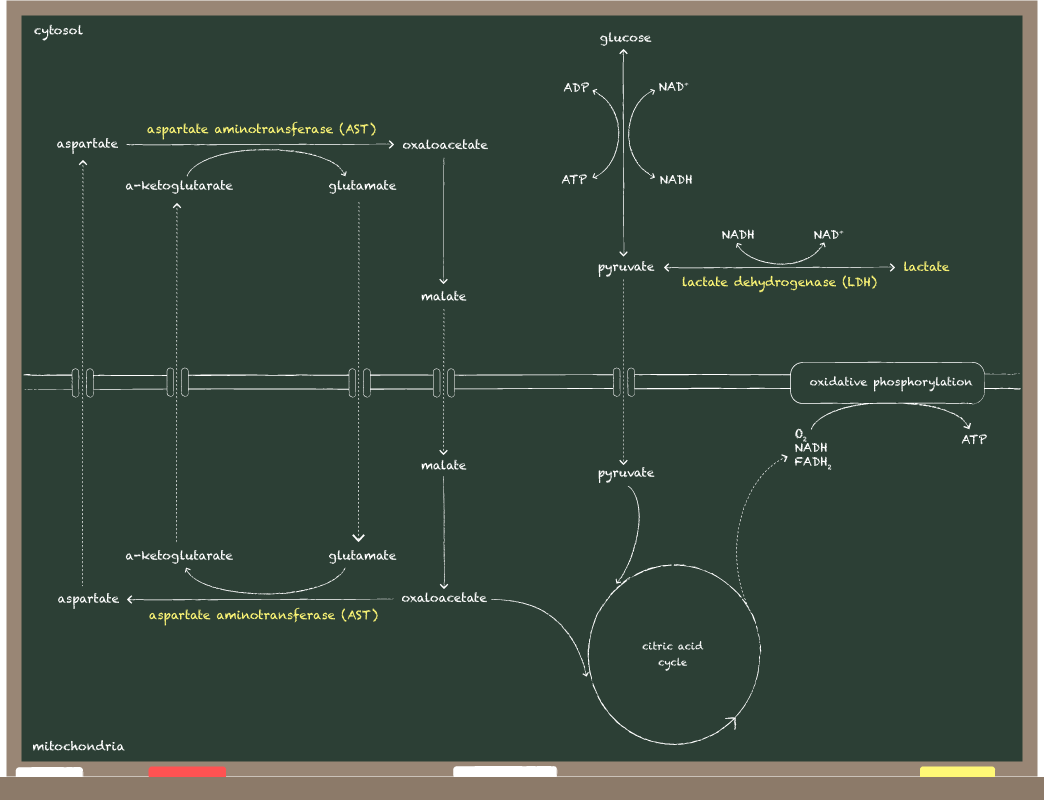
AST, LDH:
LACTATE:
✿ Hepatobiliary disorders
✧ hepatocellular damage
✧ infiltrative liver disease
✧ cholestasis
✿ Muscle disorders
✧ muscle trauma/ rhabdomyolysis
✧ strenous exercise
✧ muscular dystrophy
✧ polymyositis
✧ intramuscular injection
✿ Cardiac causes
✧ myocardial infarction
✿ Blood disorders
✧ hemolytic anemia
✿ Other
✧ pulmonary embolism
✧ acute pancreatitis
✧ renal infarct
✧ cerebral infarction
✧ seizures
✧ delirium tremens
✧ heat stroke
✧ sepsis
✧ drugs
✿ Hematologic
✧ hemolytic anemia
✧ megaloblastic anemia
✧ leukemia
✧ lymphoma
✿ Gastrointestinal
✧ ischemic hepatitis
✧ acute pancreatitis
✧ mesenteric ischemia
✿ Cardiac
✧ myocardial infarct
✿ Neurologic
✧ cerebrovascular infarct
✧ intracranial hemorrhage
✧ encephalitis/ meningitis
✿ Skeletomuscular
✧ myopathies
✧ rhabdomyolysis
✿ Autoimmune
✧ systemic vasculitides
✧ granulomatous diseases
✧ connective tissue disorders
✿ Renal
✧ renal infarct
✿ Pulmonary
✧ pulmonary embolism/ infarct
✿ Neoplastic
✧ metastatic disease
✧ tumor lysis syndrome
✧ testicular cancer
✧ sarcomas
✿ Infectious
✧ sepsis
✧ hiv & opportunistic infections
⁎ pneumocystis pneumonia (pcp)
⁎ toxoplasmosis
⁎ histoplasmosis
✧ tuberculosis
✧ malaria
✿ Drug-induced
✧ neuroleptic malignant syndrome
✧ malignant hyperthermia
✧ serotonin syndrome
✿ Other
✧ trauma
✧ shock
✿ Hypoperfusion
✧ hypovolemia
✧ shock/ sepsis
✧ cardiac arrest
✧ hypoxemia
✧ carbon monoxide poisoning
✿ Increased metabolic demand
✧ seizure
✧ malignancy
✧ hypothermia
✧ severe asthma
✿ Oxidative phosphorylation interferance
✧ cyanide poisoning
✧ drugs (salicylate, metformin)
✧ sepsis
✿ Shunting of pyruvate to lactate production
✧ alcohol intoxication
✧ liver disease
✧ type 1 glycogen storage disease
✧ pyruvate dehydrogenase deficiency
✧ drugs (beta-agonists)
✧ infection/ sepsis
✿ Mitochondrial dysfunction
✧ mitochondrial encephalomyopathy
with lactic acidosis and stroke-like episodes (melas) syndrome
✧ drugs (antivirals, propofol)
✿ Impaired lactate clearance
✧ renal failure