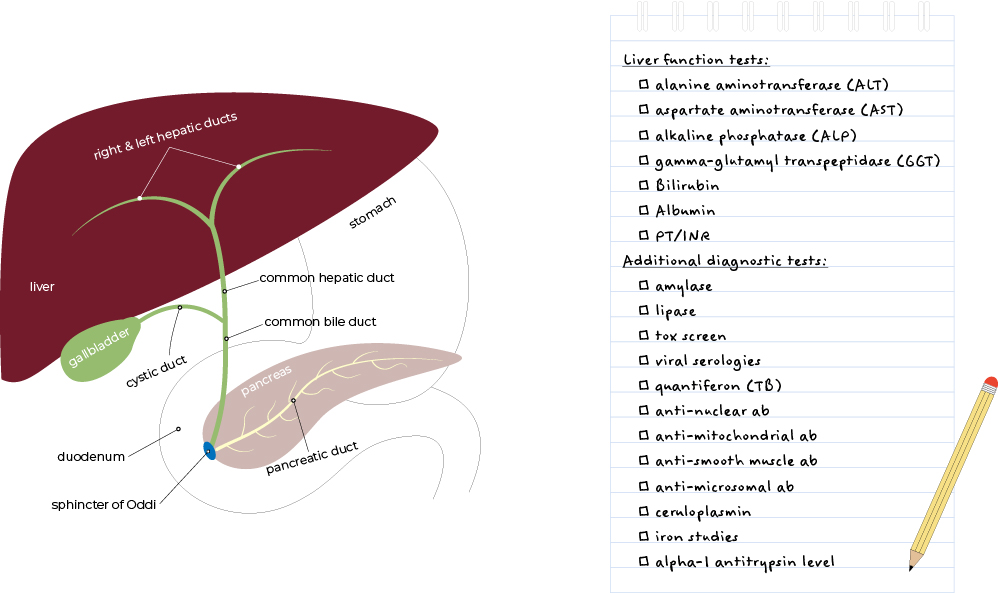
• Common tests used to evaluate liver function & diagnose liver disease include liver enzymes (AST, ALT, ALP), bilirubin (total, direct, indirect), and liver synthetic function tests (albumin, PT/INR).
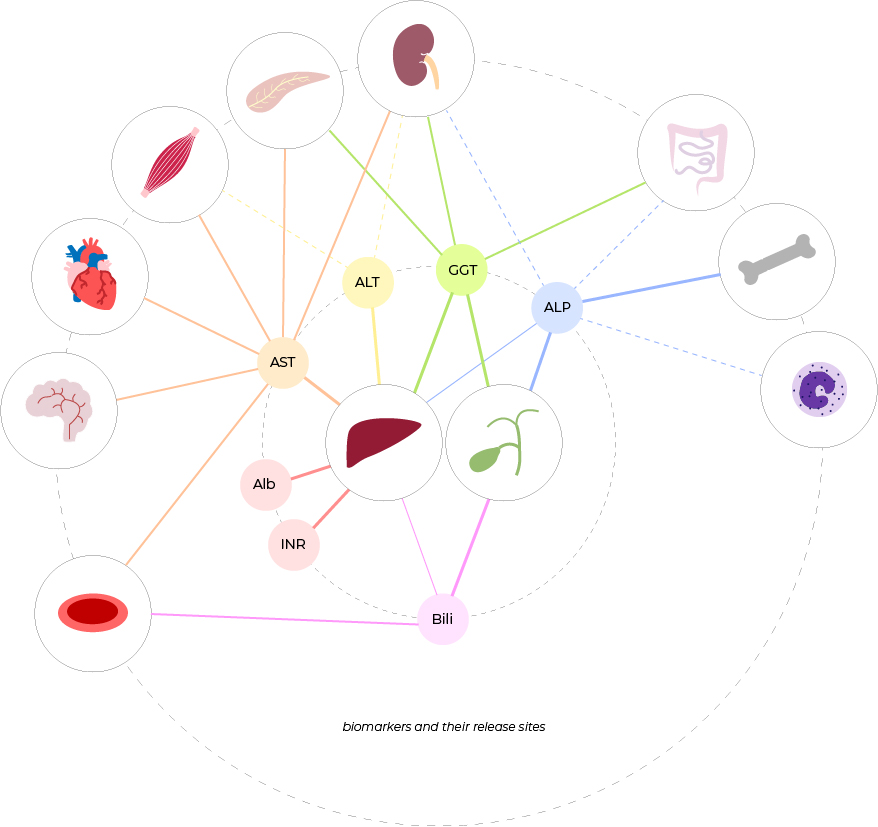
AST (aspartate aminotransferase): transfers amino groups from aspartate to α-ketoglutarate (part of citric acid cycle), found in cytoplasm & mitochondria, diffusely in hepatocytes (hence a surrogate for hepatocellular injury), heart, skeletal muscle, kidneys, brain, red blood cells, pancreas
ALT (alanine aminotransferase): transfers amino groups from alanine to α-ketoglutarate (part of citric acid cycle), found in cytoplasm, primarily in hepatocytes (hence a surrogate for hepatocellular injury), very little in kidneys, skeletal muscle
ALP (alkaline phosphatase): enzyme transporting metabolites across cell membranes, found primarily in bile duct epithelia (hence a surrogate for cholestasis) and bone, also in placenta, kidneys, intestines, leukocytes
GGT (gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase): microsomal enzyme transporting amino acid across cell membranes, found in both hepatocytes and bile duct epithelia, also in kidneys, pancreas, intestine
Bilirubin: a product of heme metabolism
Direct (conjugated): excreted from the liver down and travels the biliary tree
Indirect (unconjugated): released from red blood cells
Albumin: protein produced by the liver, carried important organic molecules in the blood
PT/INR: a measure of clotting factors produced by the liver
✿ Hepatobiliary disorders
✧ hepatocellular damage
✧ infiltrative liver disease
✧ cholestasis
✿ Muscle disorders
✧ muscle trauma/ rhabdomyolysis
✧ strenous exercise
✧ muscular dystrophy
✧ polymyositis
✧ intramuscular injection
✿ Cardiac causes
✧ myocardial infarction
✿ Blood disorders
✧ hemolytic anemia
✿ Other
✧ pulmonary embolism
✧ acute pancreatitis
✧ renal infarct
✧ cerebral infarction
✧ seizures
✧ delirium tremens
✧ heat stroke
✧ sepsis
✧ drugs
✿ Hepatobiliary disorders
✧ infiltrative liver disease
✧ cholestasis
✧ hepatocellular damage
✿ Bone disorders
✧ osteomalacia/ rickets
✧ bone malignancy
✧ skeletal trauma
✧ chronic osteomyelitis
✧ paget
✧ hereditary hyperphosphatasia
✿ Endocrine/ metabolic causes
✧ hyperparathyroidism
✧ hyperthyroidism
✧ diabetes mellitus
✧ rapid weight loss
✧ acromegaly
✿ Intestinal causes
✧ peritonitis
✧ ibd (ulcerative colitis)
✧ s/p fatty meal (blood type o, b)
✿ Other
✧ physiologic (newborns, aging)
✧ pregnancy
✧ malignancy
✿ Conjugated hyperbilirubinemia
✧ hepatobiliary cholestasis
✧ dubin-johnson syndrome
✧ rotor syndrome
✿ Unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia
✧ hemolysis
✧ dyserythropoiesis
✧ hematoma reabsorption
✧ gilbert syndrome
✧ crigler-najjar syndrome
✧ wilson disease
✧ hyperthyroidism
✧ advanced cirrhosis
✧ heart failure
✧ portosystemic shunt
✧ drugs
✿ Hepatobiliary disorders
✧ hepatocellular damage
✧ infiltrative liver disease
✧ cholestasis
✿ Hepatobiliary disorders
✧ hepatocellular damage (alcohol)
✧ infiltrative liver disease
✧ cholestasis
✿ Other
✧ pancreatic disease
✧ renal failure
✧ myocardial infarct
✧ copd
✧ diabetes mellitus
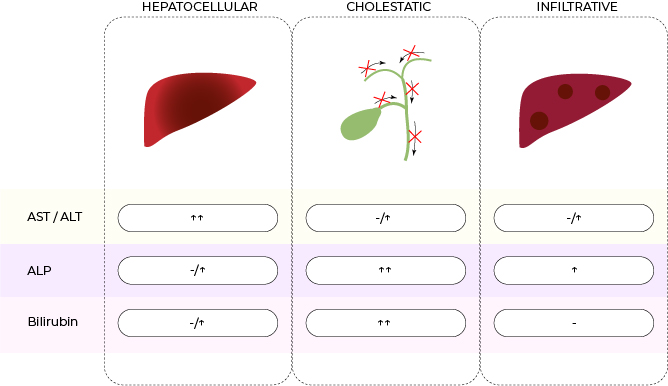
liver injury patterns
• The combinations of various liver function test values can suggest different patterns of liver pathology
Hepatocellular: damage to the hepatocytes leading markedly increased levels of aminotransferases (ALT, AST) with or without increased levels of ALP and bilirubin (due to the affected intrahepatic biliary structure).
Cholestatic: damage to the bile duct epithelia in either or both intra- and extra-hepatic regions (liver parenchyma and biliary tree) leading to increased level of ALP (found in bile duct epithelia) and of bilirubin (a marker of bile flow).
Infiltrative: deposition of organic substrates in the liver often causing isolated ALP level.
✧ viral hepatitis
✧ alcoholic hepatitis
✧ ischemic hepatitis
✧ drug (acetaminophen)
✧ toxin (mushroom)
✧ autoimmune hepatitis
✧ infectious mononucleosis
✧ congestive hepatopathy
✧ hemochromatosis
✧ wilson disease
✧ nafld
✧ alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency
✧ budd-chiari syndrome
✧ sinusoidal obstructive syndrome
✧ hellp
✧ choledocholithiasis
✧ cholangitis
✧ cholecystitis
✧ gallstone pancreatitis
✧ obstructive mass
✧ primary sclerosing cholangitis
✧ primary biliary cholangitis
✧ post-ercp
✧ biliary stricture
✧ infection (liver flukes, hiv)
✧ intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy
✧ benign postoperative cholestasis
✧ drug/ toxin
✧ total parenteral nutrition
✧ amyloidosis
✧ lymphoma
✧ mets to liver
✧ granulomatous disease
✧ tuberculosis
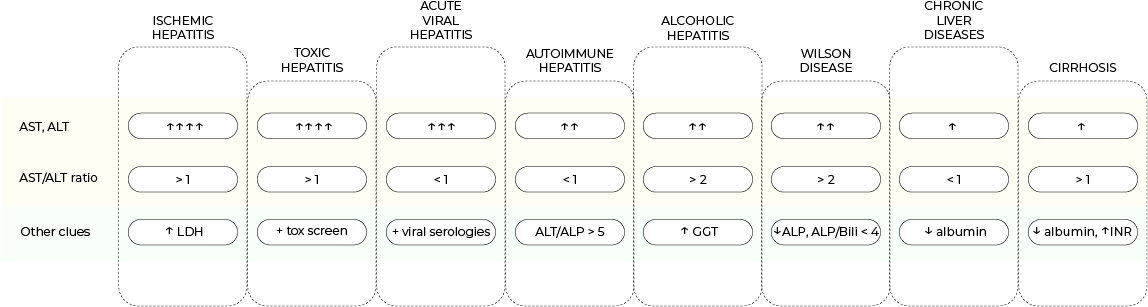
ast:alt ratio
• The level and ratio of AST and ALT vary in different liver conditions hence can be used as diagnostic clues.
• Aminotransferases are markedly elevated in acute/ fulminant liver injury caused by ischemia, drug/ toxin (acetaminophen, mushroom poisoning), and viral hepatitis; and to a lesser degree, alcohol abuse, autoimmune hepatitis, Wilson disease, and HELLP syndrome.
• Aminotransferases are mildly elevated in chronic liver conditions that are well-compensated; however, albumin is often low in chronic states.
• ALT is often higher than AST in most liver diseases except for acute ischemic/ toxic hepatitis, alcoholic liver disease, cirrhosis, and WIlson disease.
• Elevated PT/INR is a marker of declined liver synthetic function and is often seen in acute fulminant liver failure and end-stage liver disease such as cirrhosis.
• GGT is a useful marker to confirm alcoholic iiver disease.