
• Immunoglobulins (Igs) are γ-globulins, the most common types of globulins in the blood; therefore an elevation in Igs (hypergammaglobulinemia) often raises the total protein level and might cause significant clinical symptoms.
• Igs are antibodies which play important roles in humoral immune response.
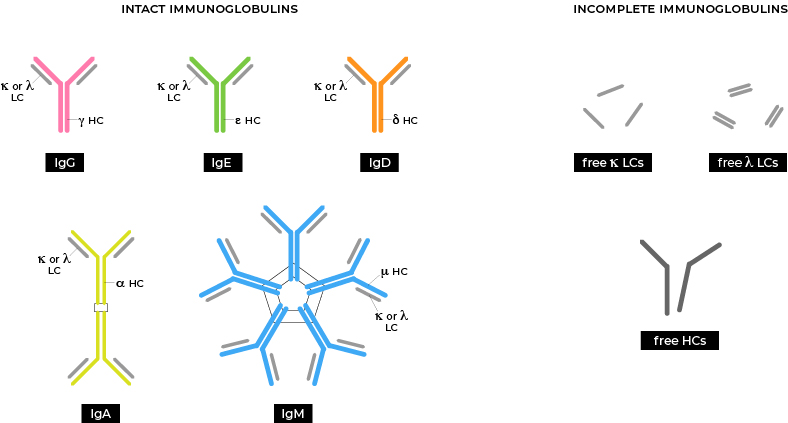
• A normal Ig is composed of 2 heavy chains (HCs) and 2 light chains (LCs).
• There are 5 major types of HCs (γ, ε, δ, α, and μ) and 2 types of LCs (κ and λ).
• There are 5 major Ig isotypes, classified based on 5 major types of HCs:
IgG = 2 γ HCs + 2 LCs (either κ or λ)
IgE = 2 ε HCs + 2 LCs (either κ or λ)
IgD = 2 δ HCs + 2 LCs (either κ or λ)
IgA = 2 α HCs + 2 LCs (either κ or λ)
IgM = 2 μ HCs + 2 LCs (either κ or λ)
• IgG, E, D exist as single monomer; whereas, IgA exist as a dimer and IgM as a pentamer.
• IgG has 4 subclasses (IgG1-4) and IgA has 2 subclasses (IgA1-2).
• Free LCs (either κ or λ) and free HCs (either γ, ε, δ, α, or μ) are incomplete Igs that can be detected in the blood at high concentration, which might suggest certain underlying pathological processes.
hypo- & hyper-gammaglobulinemia
• Hypogammaglobulinemia is classified into panhypogammaglobulinemia and selective hypogammaglobulinemia.
Panhypogammaglobulinemia: a decrease in most, if not all, Ig isotypes-- either caused by a primary disorder (hereditary condition wherein Ig production is impaired) or an acquired condition such as protein loss (via renal tubule, GI tract, or lymph channels) or drug-mediated Ig destruction
Selective hypogammaglobulinemia: a decrease in one specific Ig isotype either due to a primary deficiency, a suppresion of its production due to overproduction of other Ig isotype (e.g. hyper-IgM syndrome causing IgG, IgA, and IgE deficiencies), or an increased consumption in enhanced immune activity (e.g. IgG deficiency in chronic infection and autoimmune disorders)
• Hypergammaglobulinemia is a common cause of hyperproteinemia and it can be a manifestation of either a monoclonal or polyclonal gammopathy.
Monoclonal gammopathy:
Polyclonal gammopathy:
PANHYPOGAMMAGLOBULINEMIA
✿ Inherited disorders
✧ common variable immunodeficiency
✧ severe combined immunodeficiencies
✧ x-linked agammaglobulinemia
✧ autosomal agammaglobulinemia
✧ transient hypoimmunoglobulinemia of infancy
✧ mhc class ii deficiency
✧ bloom syndrome
✧ comel-netherton syndrome
✿ Acquired disorders
✧ protein loss
☼ protein-losing gastroenteropathy
☼ nephrotic syndrome
☼ peritoneal dialysis
☼ intestinal lymphangiectasia
☼ chylothorax
☼ thoracic duct leak or drainage
☼ erythroderma
✧ drugs
☼ chemotherapy
☼ immunosuppressants
☼ antirheumatics (gold, d-penicillamine, sulfasalazine, rituximab)
☼ anticonsulvants (phenytoin, carbamazepine)
SELECTIVE HYPOGAMMAGLOBULINEMIA
✿ IgG deficiency
✧ selective (inherited) IgG deficiency
✧ ataxia-telangiectasia
✧ hyper-IgM syndrome
✧ atopic disease
✧ chronic lung diseases (asthma, copd)
✧ autoimmune disorders (sle, vasculitis)
✧ growth hormone deficiency
✧ chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis
✧ hiv/aids
✿ IgA deficiency
✧ selective (inherited) IgA deficiency
✧ ataxia-telangiectasia
✧ hyper-IgM syndrome
✿ IgM deficiency
✧ selective (inherited) IgM deficiency
✧ wiskott-aldrich syndrome
✧ dock8 deficiency (hyper IgE syndrome)
✿ IgE deficiency
✧ selective (inherited) IgE deficiency
✧ hyper-IgM syndrome
MONOCLONAL GAMMOPATHY
✿ B cell / plasma cell disorders
✧ monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (mgus)
☼ IgM mgus
☼ non-IgM mgus
☼ light chain mgus
✧ monoclonal gammopathy of renal significance
✧ smoldering myeloma
✧ multiple myeloma (mm)
☼ IgG > IgA >> IgM, IgD mm
☼ light chain mm
☼ non-secretory mm
☼ oligo-secretory mm
✧ IgM myeloma
✧ osteosclerotic myeloma (poems syndrome)
✧ solitary plasmacytoma
✧ waldenstrom macroglobulinemia
✧ al (light chain) amyloidosis
✧ ah (heavy chain) amyloidosis
✧ light chain deposition disease
✧ heavy chain diseases
☼ α (malt)
☼ γ (lymphoplasmacytoid lymphoma)
☼ μ
✧ tempi syndrome
✧ chronic lymphocytic leukemia
BICLONAL GAMMOPATHY
✿ Plasma cell disorders
✧ biclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance
✧ biclonal multiple myeloma
POLYCLONAL GAMMOPATHY
✿ Acquired disorders
✧ chronic liver disease
✧ autoimmune diseases
☼ systemic lupus erythematosus
☼ rheumatoid arthritis
☼ sjogren syndrome
☼ systemic vasculitis
☼ cold agglutinin disease
☼ dermatomyositis
☼ inflammatory bowel disease
✧ chronic infection
☼ hepatitis (hcv, hbv)
☼ hiv/aids
✧ lymphoproliferative diseases
✧ myelodysplasia
✧ proliferative glomerulonephritis