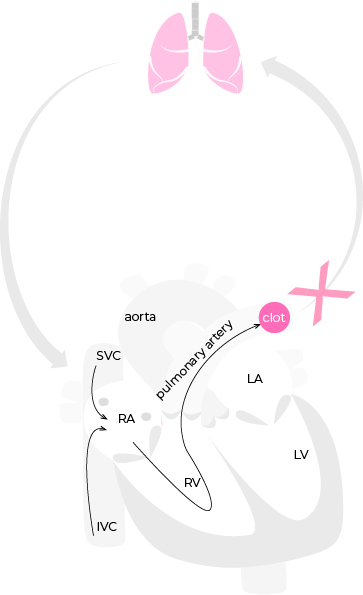
• The most frequent sign of pulmonary embolism is sinus tachycardia due to the compensatory increase in heart rate in response to the decreased cardiac output as a result of blood clot obstructing pulmonary artery outflow.
• The mechanical obstruction of the pulmonary artery also leads to pressure build up in the right ventricle and right atrium and ECG changes reflecting signs of right heart strain including:
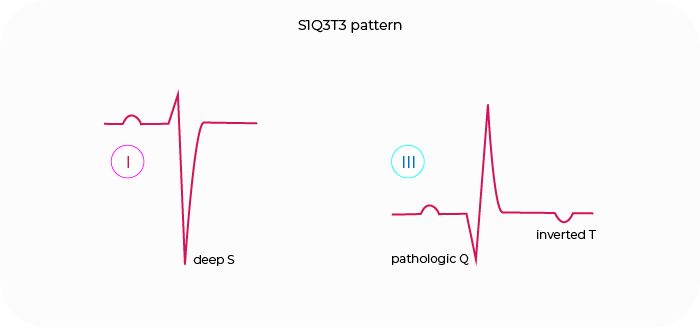
S1Q3T3 pattern (McGinn-White triad)
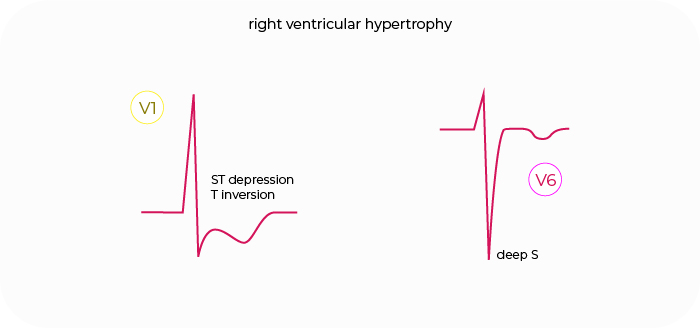
Right ventricular hypertrophy
Right atrial enlargement
Right axis deviation
Right bundle branch block
• In addition, the overstretched atria and ventricles are prone to various types of arrhythmia such as:
Atrial arrhythmias (e.g. atrial tachycardia, atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter)
AV block
Ventricular arrhythmias (e.g. ventricular tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation)