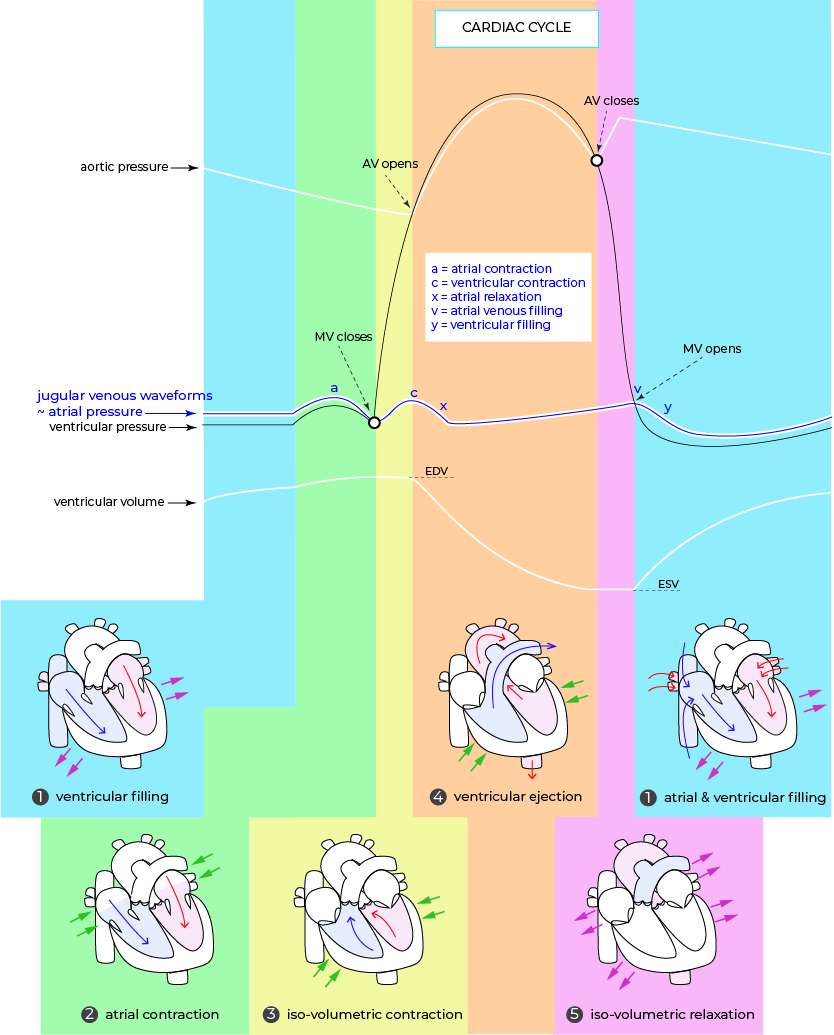
• Elevated “a” wave: occurs when there is an opposing resistance as RA empties in to RV due to-
pulmonary hypertension
tricuspid stenosis
RA mass or thrombus
• Cannon “a” wave: prominent venous pulse occurs when RA contracts against a close tricuspid valve due to-
premature atrial contraction in-
premature atrial/ junctional/ ventricular beats
AV dissociation in-
complete AV block
ventricular tachycardia
• Absent “a” wave: occurs when RA doesn’t forcefully contract due to-
atrial fibrillation
• Elevated “x” wave (Friedrich’s sign): occurs when RA can’t fully relax due to-
constrictive pericarditis
• Elevated “v” wave: occurs when the RV contracts but blood regurges back to RA & increases RA pressure in-
tricuspid regurgitation
• Kussmaul’s sign: neck veins rise during inspiration due to-
tamponade
right heart failure
acute RVMI
cannon a waves
• Elevated “a” wave: occurs when there is an opposing resistance as RA empties in to RV due to-
pulmonary hypertension
tricuspid stenosis
RA mass or thrombus
• Cannon “a” wave: prominent venous pulse occurs when RA contracts against a close tricuspid valve due to-
premature atrial contraction in-
premature atrial/ junctional/ ventricular beats
AV dissociation in-
complete AV block
ventricular tachycardia
giant c-v waves
• Elevated “v” wave: occurs when the RV contracts but blood regurges back to RA & increases RA pressure in-
tricuspid regurgitation
kussmaul's sign
• Elevated “x” wave (Friedrich’s sign): occurs when RA can’t fully relax due to-
constrictive pericarditis
• Kussmaul’s sign: neck veins rise during inspiration due to-
tamponade
right heart failure
acute RVMI